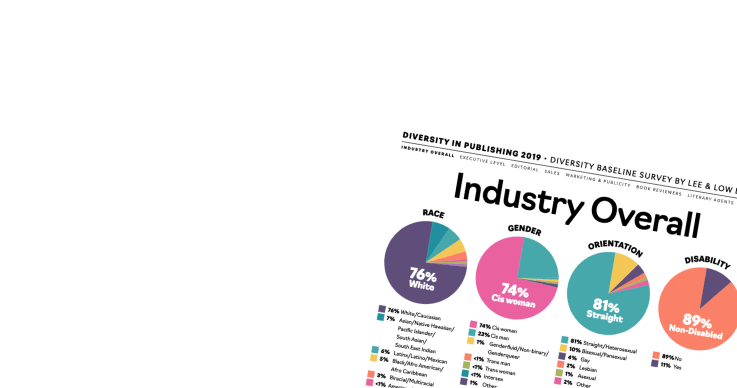
Over the weekend (Feb. 7), I taught a breakout session at the Annual Winter Conference of the Society of Children’s Book Writers and Illustrators here in New York, NY. We were discussing how to write for a diverse audience. My main focus was on helping the audience to remember that no matter what you’re writing, your audience will always be diverse. Too often, writers think that there’s a dichotomy–that there are “multicultural books” that are read by kids of color, and that “everyone else” (meaning, white kids) read “mainstream” (meaning, white) books.
This just isn’t the case. Readers tend to read widely, and kids of color are just like their white peers, reading the most popular books, the books assigned to them in schools, and whatever else they happen to come across that sounds interesting to them.
 Below are the links and a few notes from the handout I gave to writers at the conference, with a few annotations to clarify what we were talking about. I hope it is a useful resource when you’re thinking of writing for a diverse audience (i.e., when you’re thinking of writing–period!). If you have any further ideas–or links where writers can go further in depth–please add them in the comments.
Below are the links and a few notes from the handout I gave to writers at the conference, with a few annotations to clarify what we were talking about. I hope it is a useful resource when you’re thinking of writing for a diverse audience (i.e., when you’re thinking of writing–period!). If you have any further ideas–or links where writers can go further in depth–please add them in the comments.
Other coverage: SCBWI Conference Blog
Other sessions on the same topic: Newbery Medalist Kwame Alexander’s breakout session on writing diverse books
Seven Essentials You Need to Know about Writing for a Diverse Audience
- Don’t feel “forced” to write diversity, but remember your readers are diverse
- If your real-life world isn’t diverse, if you don’t know any people of color, if you don’t know how to write diverse characters without relying on stereotypes, you don’t have to feel pressured to do so.
- And don’t feel like you need to come in and “save” anyone—come in from a position of equality and seeking equity.
- However, your world is likely more diverse than you think.
- Often, people of color and Native Americans are most hurt by passing comments in books that aren’t “about” POC at all. (Debbie Reese’s blog has many examples of this.)
- Don’t be afraid to discuss race. If you’re new at this, do a lot of listening.
- You need to know about power dynamics
- What is a microaggression?
- See a definition and examples at The Microaggressions Project
- Remember that these can show up in your writing even when not writing “about” POC/LGBT/disabled people. Be mindful. Treat minor characters like real people, not caracatures/stereotypes.
- Microaggressions in Librarianship
- White (and other) privilege
- Writing across POC cultures—what is the individual dynamic?
- Expand your definition of “diversity.”
- Diversity is not just about race, religion, class, etc. It is often about how many different identity markers come together to create a specific experience. Here’s a basic definition of intersectionality. Think about how it affects your characters.
- Intersections happen across 11 lenses, according to Teaching Tolerance:
- race
- ethnicity
- language
- immigration
- religion
- gender identification
- sexual orientation
- class
- ability
- age
- place
- Social media doesn’t have to be a distraction.
- Check out these excellent feeds & related blogs for listening and learning (many also have great diverse book lists!):
- Lee & Low and Tu Books: blog, @tubooks, @leeandlow
- Diversity in YA, @diversityinYA
- We Need Diverse Books, @diversebooks
- Rich in Color, @richincolor
- American Indians in Children’s Literature, @debreese
- Black Girl Nerds, @blackgirlnerds
- Disability in Kidlit, disabilityinkidlit.tumblr.com, @disabilityinlit
- Twitter searches: #WeNeedDiverseBooks, #BlackLivesMatter
- Angry Asian Man
- Disgrasian: @disgrasian
- Ebony Elizabeth Thomas & The Dark Fantastic, @ebonyteach
- Ta-Nahisi Coates, @tanehisicoates
- Racialicious, racialicious.tumblr.com, @racialicious
- Colorlines, @colorlines
- Mitali Perkins, @mitaliperkins
- Cynthia Leitich Smith & Cynsations, @CynLeitichSmith
- NPR Code Switch, @nprcodeswitch
- Roxane Gay, @rgay
- In your writing, seek both the universal & the specific.
- Universal stories appeal to a broad swath of readers: characters dealing with parents, love stories, stories of loss—these are all stories of the human condition.
- Specific details make your story richer.
- If you are writing cross-culturally, do your research. Debbie Reese has an excellent guide on seeking a cultural expert in Native American issues. Look for similar information on the culture you’re writing about.
- And write a good book:
- the most important thing about a diverse book is the same thing as for all books. What matters most:
- Characterization
- Plot
- World-building
- Pacing
- Age-appropriate content (though not shying away from edgy topics)
- Concept
- the most important thing about a diverse book is the same thing as for all books. What matters most:
- Contextual clues are better than exposition of culture.
- Show, don’t tell!
- Remember that your audience includes cultural insiders and outsiders. Balance enough information for outsiders with the possibility of boring insiders with too much basic everyday information.
- School visits are a great way to reach diverse students.
- At the beginning of your career, be willing to do school visits or Skype visits for a low honorarium, until you can build up your resume and network with more teachers.
- Keep in mind that schools with a high percentage of diverse students are often the most underfunded. They may not have a budget for an honorarium, but may be able to purchase books for students to compensate.
 Stacy Whitman is Editorial Director and Publisher of Tu Books, an imprint of LEE & LOW BOOKS that publishes diverse science fiction and fantasy for middle grade and young adult readers.
Stacy Whitman is Editorial Director and Publisher of Tu Books, an imprint of LEE & LOW BOOKS that publishes diverse science fiction and fantasy for middle grade and young adult readers.